Otico
Shaping the future of Otoscopy in Indian healthcare
Overview
Reimagining video otoscopes for India's ENT market to overcome the challenges of traditional pocket otoscopes in maintaining digital records, accurate diagnosis, & serving remote areas.
At a glance
My contribution
Worked with
Live project with
Keon Design
Design Research
Primary research & secondary research
Year & timeline
2018, 1.5 months
Feature mapping
Features for interface & physical product
Team
4 Product design students
Scope
Product and UX/UI design
Form study
Brainstorm, mockups
& CAD models
About otoscope
Otoscope is a medical instrument used to diagnose ears for infection, inflammation and other issues. An otoscope consists of a handle and a head.
There are four types of Otoscopes:
Pocket Otoscope
Wall mounted otoscope
Open head wall mount otoscope
Close head wall mount otoscope
Video otoscope
Research analysis
We visited 20 hospitals/clinics and observed few of their appointments.
Current tool usage
Most ENT doctors in India rely on pocket otoscopes as their primary diagnostic tool, which consists of a basic torch attached to a magnifying lens providing
2-4 times magnification.
Diagnostic Process
For comprehensive diagnosis, doctors must use both an otoscope and endoscope together, with the latter enabling patients to view their condition on a screen for
better understanding.
Ergonomic Challenges
While the otoscope requires a pen-like grip for operation, doctors often struggle with hand-eye coordination, necessitating the use of the patient's cheek as a stabilizing support during examination.
Technology adoption
The technological receptiveness among Indian ENT practitioners shows distinct segments. While 40% embrace new medical technologies, 33% prefer traditional methods, and 27% remain neutral about technological advancements in their practice.
Dr Neerja Rao, Ruby Hall Hospital
“There is no proper mechanism for recording data of the patient and recording every diagnosis becomes a burden for the hospital”
Dr Danish, Ruby Hall Hospital
““The endoscope requires a huge set up and hence diagnosis cannot be done in remote places””
Task flow
Otoscope analysis duration: 12 mins
Endoscope analysis duration: 10 mins
User Challenges
-
The doctors are forced to use 2 medical devices: endoscope and otoscope for even basic ear checkups, which can unnecessarily increase the appointment time.
-
Once the doctor checks a patient, they do not have a way to save the images/videos in the patient records or atleast explain the patient what is wrong with them.
-
Doctors are able to carry only their pocket otoscopes to villages/remote areas, which leads to non-conclusive checkups.
So based on the user challenges and research analysis,
I came up with the following opportunity statement
How might we create an ergonomic video otoscope that aligns with Indian ENT doctors' clinical practices while enabling better record-keeping and remote care capabilities?
Form & interface explorations
Introducing Otico
A digitally enhanced video otoscope that streamlines ENT examinations through ergonomic controls, continuous imaging, and integrated patient record management. The device features ambidextrous operation, automated hygiene prompts, and seamless data synchronization between examination room and reception, enabling efficient digital documentation of patient diagnoses.
The interface
Connecting to wifi and laptop
The doctor’s computer is connected with the receptionist’s computer, and as soon as a is let in the cabin for a checkup, the patient’s records can appear on the doctor’s computer. If required they can sync that data to the otoscope as well.
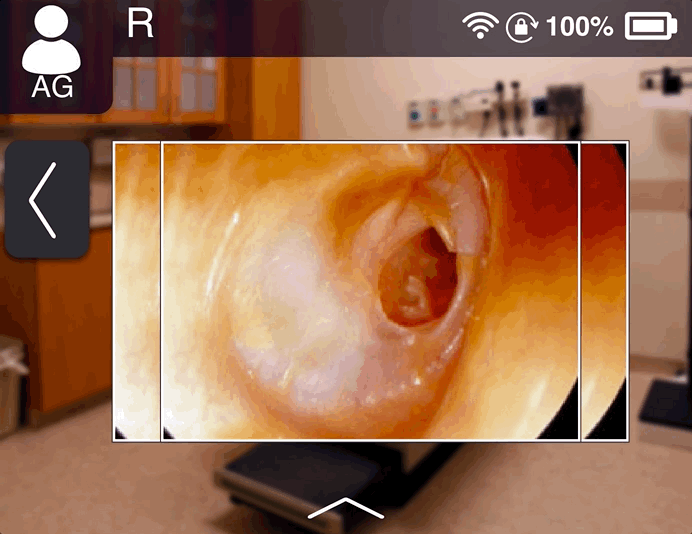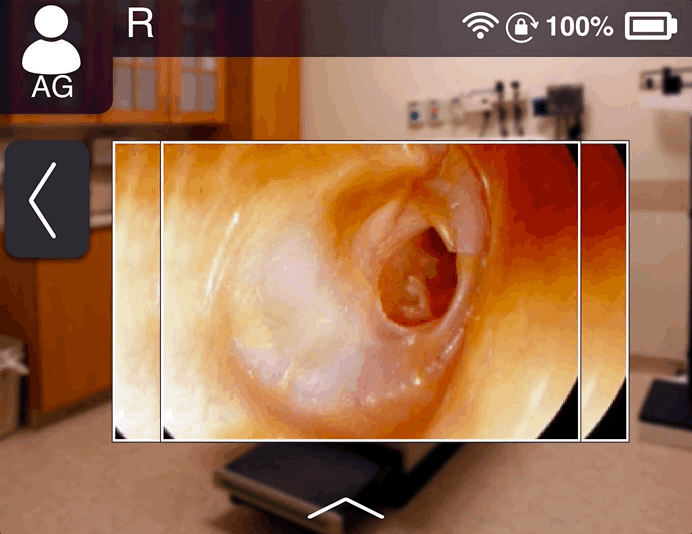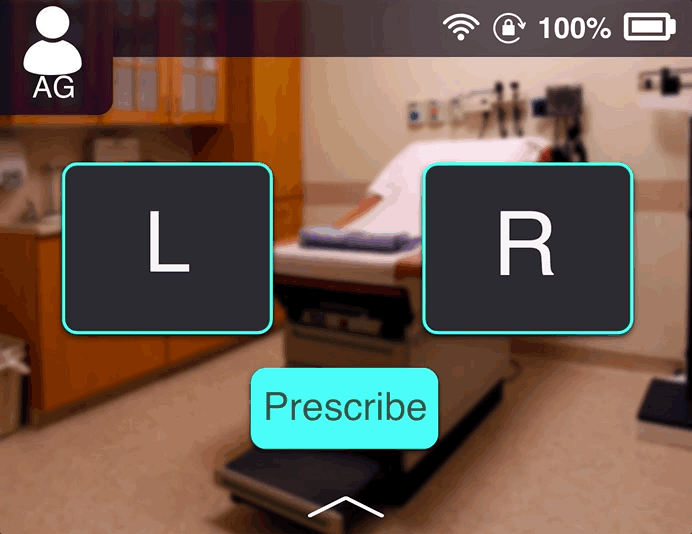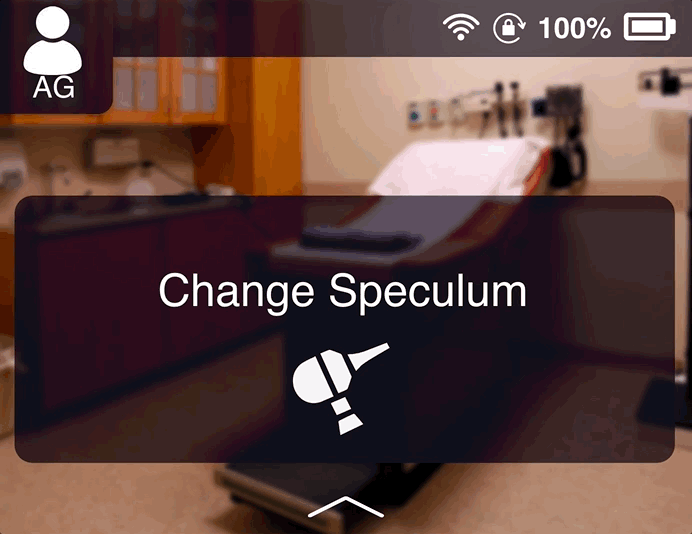
Recording and taking images
The doctor can take images and record video if required and transfer them to computer to maintain the
patient’s records.
Changing speculum
After one checkup, the doctor will be nudged to change the otoscope’s speculum.
Homescreen
Camera will be on in the background for the main screen. which can reduce some time for the doctor.
The product
Ergonomics
Trackpad placement
The trackpad is placed such that, the thumb is able to move around, without loosening the grip.
Zoom in zoom out placement
The zoom in zoom out is placed at the back, so that the doctor can operate that with their index finger.
Form
The form of the product is made in a way that it comfortably fits in the doctor’s hands.
User testing
We made test testing protocol and showed the product to
5 doctors.
The doctors appreciated that they will be able to save pictures in the otoscope which will help them save records of patients.
They also commented that now they will be able to do checkups in shorter duration, and have a faster diagnosis.
They also liked the fact that the otoscope was light in weight and they could carry it in remote areas.
What I learned?
This was one of the first projects where I learned about UX/UI and different concepts used in it.
We did a lot of extensive primary user research, which taught me a lot about research analysis methods.